Surface Finishes for PCBs
Different types of surface finishes for your PCBs
The electric connection on a PCB depends solely on the conductivity of the copper – and therefore it must be well protected, to be able to function to its full potential, for as long as possible.
That is why the choice of surface finishes for your PCBs are such an important one, that can affect the end product in many ways.
The surface finish is responsible for two key areas when it comes to the performance of your PCBs; to protect the copper from oxidation and to provide a surface for high solderability for when components are to be assembled on your PCBs, to provide a reliable and long lasting end product.
There are a few surface finishes to choose from, and we want to make it as easy for you as possible. Down below we have listed the different types, along with a pros and cons list for each of them. And to create the ultimate overview – a table near the end.
HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling)
Pros of HASL Surface Finish:
- Excellent wetting during component soldering
- Copper corrosion avoided
Cons of HASL Surface Finish:
- Low planarity on vertical levelers leads HASL unacceptable for fine pitch components
- High thermal stress during process causes defects into circuit board
It’s also important to note that in order to be in line with regulations concerning environment protection, HASL has developed into two subcategories: Lead HASL and Lead-free HASL. The Lead-free variety follows the law and regulations of RoHS (restrictions of hazardous substances) which are guidelines, first adopted by the EU.
ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold)
Pros:
- Flat surface
- Simple process mechanism
- High temperature resistance
- Suitable for lead-free soldering
- Suitable for SMT
- BGA (ball grid array) etc.
ENIPIG (Electroless Nickel Electroless Palladium Immersion Gold)
Pros:
- Capable of withstanding excellent multiple reflow cycles
- Very reliable wire bonding capability
- Capable of meeting strict requirements of multiple types of packages including;
- THT
- SMT
- BGA (ball grid array)
- Wire bonding
- Press fit etc.
ENIG & ENEPIG advantages
ImSn (Immersion Tin)
The advantages when dealing with ImSn consists of an extremely planar finish on the copper pads, and therefore makes it a suitable choice for SMT application. And due to its surface, it is also easily detectable by Automated Optical Inspection techniques.
OSP (Organic Solderability Preservatives)
Pros of OSP Surface Finish:
- Flat/planar
- Short, easy process cycle
- Inexpensive
- Reworkable
- Not affect finished hole size
- Copper/tin solder joint
Cons of OSP Surface Finish:
- Multiple reflows
- Short shelf life
- Not conductive
- Difficult to inspect
- Limited thermal cycles
However, due to the short shelf life (depending on the environment, temperature and humidity of where it’s stored) it requires thorough planning! As soon as the OSP layer breaks, there will be direct contact to the copper in the pads which will then start corroding.
Meaning that this is not a surface finish we recommend – unless you have all of your components on stock and are ready to assemble as soon as the PCBs have been produced.
Another thing to consider is reflow soldering. This surface finish can become problematic if the board needs to go through reflow several times. Which is often the case with PCBs that have components on the top and as well as the bottom.
What to keep in mind when deciding on a specific surface finish
Cost
Corrosion resistance
In-circuit testing (ICT)
Hole fill
How to choose a surface finish
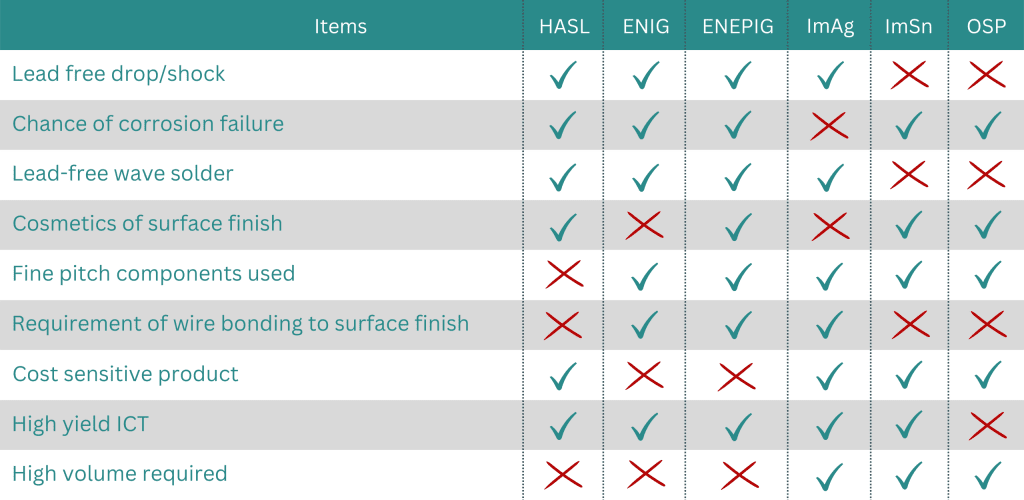
To help your team make a decision regarding surface finish, have a look at the table below. The table factors in the attributes each type of surface finish has and does not have.
Making the right choice
We can help you with the production and advice regarding your PCBs. You can read more about our PCB solutions here, we also provide components procurement and assembly.
Or you can get in touch with us directly, by clicking below.
